
14 June 2024
Insect protein plays an important role in future food security, providing rich nutritional content and little environmental impact given their high feed conversion efficiency. We think the insect protein market will grow with the increasing risk of food insecurity driven by extreme weather events.

Source: Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations
Insects could be the key to resolving malnutrition and future food insecurity problems exacerbated by climate change. They’re widely available and offer ample macronutrients and micronutrients. In addition, insect farming requires fewer natural resources, while generating less waste and emissions compared to conventional livestock farming.
We think consuming insects as a major protein source, instead of livestock, could help mitigate the environmental impact of the agricultural sector. It also allows the global food system to adapt to changes brought about by climate change.
Governments are aware of the risks and opportunities that increasing the consumption of insects in diets could bring. Poland is proposing an ‘anti-bug’ law that requires a warning label on food products containing insects, while Italy now requires strict labelling of the use of insect flour in traditional food products such as pasta and pizza. Some places are more receptive: Singapore and the EU, for example, have approved certain insects for human consumption. However, the acceptance of edible insects varies across regions and cultures.
The increase in occurrence of extreme weather events will lead to a shrinking supply of animal-based protein. Insect protein can be an alternative. However, the ‘yuck factor’ remains a concern. Researchers have found that when the natural form of insects is hidden in familiar foods, consumers are less resistant to consuming them[@why-esg-matters-03-01]. For example, cupcakes made with cricket flour tend to be more acceptable than a cricket lollipop.
Percentage of recorded edible insect species per group globally
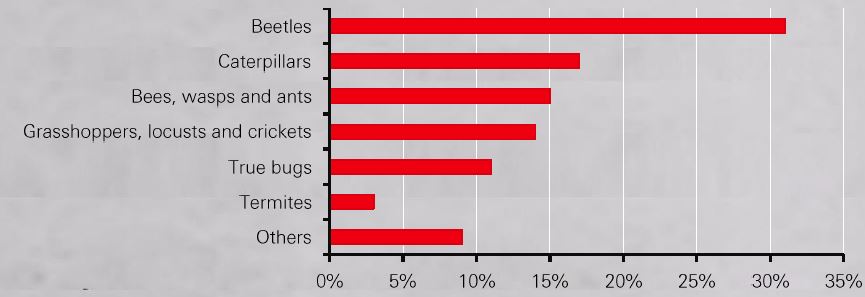
Note: True bugs: a hemiptera is an order of insects commonly called 'true bugs', comprising over 80,000 species within groups such as cicadas, aphids & planthoppers. Source: Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations
Eating insects might be an ideal solution for some of the food insecurity problems we face. For example, extreme weather worsens the severity of swarming locusts and exacerbates food insecurity in Africa. Swarming locusts used to be eaten by humans and animals during locust outbreaks when crops were destroyed.
However, due to extensive use of insecticides, the consumption of locusts is not recommended nowadays. In many developed countries, the safe harvesting of locusts for humans and animals could serve as a more sustainable management method compared to the use of insecticides[@why-esg-matters-03-02].
Animal-based protein is becoming more expensive, largely driven by years of drought conditions and inflation in the cost of feed and fuel. Compared to animal-based protein, insect protein is more efficient and reliable for human consumption, with around 80% of insects being edible vs c50% for livestock. In addition, insects’ energy conversion rate from feed to edible weight is significantly higher than livestock, their abundance is high while their reproduction cycle is shorter than vertebrates. As a result, the supply of insect protein is more scalable.
Insects provide all the essential amino acids for human nutrition. Yet, some insects have high sodium content and high saturated fat[@why-esg-matters-03-03]. The sodium content of an adult cricket is more than double that of beef or pork. Thus, if insects are to replace conventional livestock to prevent diseases related to over-nutrition in the community, we need to be aware of any downsides.
Edible insects and livestock – nutritional value
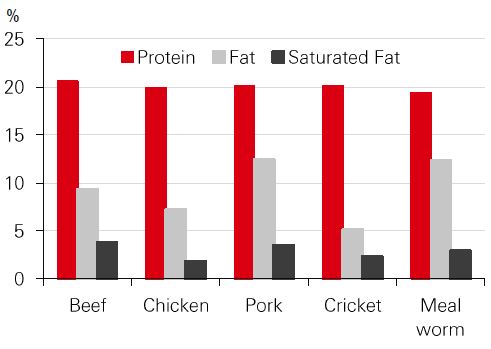
Source: European Journal of Clinal Nutrition
Edible insects and livestock – vitamin and mineral content
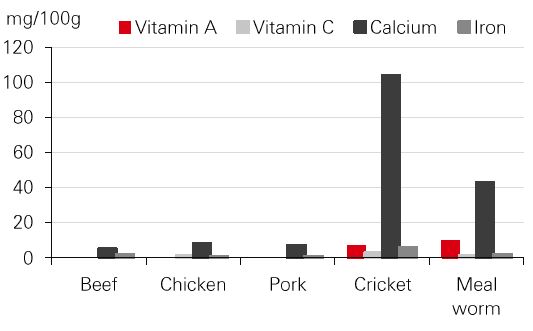
Source: European Journal of Clinal Nutrition
Apart from insects’ high nutritional value, the circularity and resilience of the insect food system make edible insects a means to fight food insecurity. Insects can transform food waste into nutritious biomass, while insect frass can be used as a fertiliser. Farming insects has little dependency on other external factors and the insect food system, making the insect food system highly sustainable.
Insect farming can lead to negative impacts on the environment if it’s performed inadequately. Some insects aren’t suited to be farmed in a captive and enclosed environment. The living condition of insects should be optimal for their species, otherwise, it might cause fighting and induce stress. Also, farming non-native insect species might harm domestic biodiversity. Regulators should look into species-specific measures to ensure insects’ welfare is protected.
It would require the elimination of the ‘yuck factor’ towards eating insects to successfully promote them as a common protein source. Many would see insects as a symbol of rot and pestilence. In order to gain broader public acceptance of insect consumption, researchers have been trying out different strategies. For example, edible insects have been served in school meals in four primary schools in Wales as researchers explore young people’s attitudes to alternative proteins[@why-esg-matters-03-04].
Also, consumers are found to be more willing to try insects when their natural shape is hidden and they’re incorporated into foods they’re familiar with, such as grounded insects being blended into baked goods or protein shakes[@why-esg-matters-03-05]. There is growing variety and supply of insect- infused food in the market to cater to different dietary preferences and understand consumer acceptance.
The flavour profile of edible insects

Source: Institute of Culinary Education
Governments are starting to recognise the importance of insect protein in future diets. Regulators are stepping in to oversee the novel food industry and build consumer trust. The Singapore Food Agency, for example, has given approval for 16 species of insects (including crickets, silkworms and grasshoppers) for human consumption from 2H 2023. In the EU, four applications for insects for human consumption have been approved, with eight more applications pending authorisation.
However, there’re still concerns over the safety of directly eating edible insects or eating livestock that are fed by insects. Insects can host microorganisms and some can do harm to humans. Regular updates on regulatory frameworks and controls over production and marketing can drive the expansion of the edible insect market by building consumer confidence.
Despite all the environmental benefits of eating insects, it would require a change in consumer psychology for insects to become one of the major protein sources. Concerns mostly revolve around the ‘yuck factor’ of eating insects and food safety. These are just some factors that need to be resolved to promote insects as a mainstream protein. However, we think the growing severity of the climate crisis and food insecurity will push countries to reconsider the food system and pay closer attention to the development of insect protein. We believe insect protein will play a more important role in our diets in the near future.




1. This report is dated as at 30 May 2024.
2. All market data included in this report are dated as at close 29 May 2024, unless a different date and/or a specific time of day is indicated in the report.
3. HSBC has procedures in place to identify and manage any potential conflicts of interest that arise in connection with its Research business. HSBC’s analysts and its other staff who are involved in the preparation and dissemination of Research operate and have a management reporting line independent of HSBC’s Investment Banking business. Information Barrier procedures are in place between the Investment Banking, Principal Trading, and Research businesses to ensure that any confidential and/or price sensitive information is handled in an appropriate manner.
4. You are not permitted to use, for reference, any data in this document for the purpose of (i) determining the interest payable, or other sums due, under loan agreements or under other financial contracts or instruments, (ii) determining the price at which a financial instrument may be bought or sold or traded or redeemed, or the value of a financial instrument, and/or (iii) measuring the performance of a financial instrument.
This document or video is prepared by The Hongkong and Shanghai Banking Corporation Limited (‘HBAP’), 1 Queen’s Road Central, Hong Kong. HBAP is incorporated in Hong Kong and is part of the HSBC Group. This document or video is distributed and/or made available, HSBC Bank (China) Company Limited, HSBC Bank (Singapore) Limited, HSBC Bank Middle East Limited (UAE), HSBC UK Bank Plc, HSBC Bank Malaysia Berhad (198401015221 (127776-V))/HSBC Amanah Malaysia Berhad (20080100642 1 (807705-X)), HSBC Bank (Taiwan) Limited, HSBC Bank plc, Jersey Branch, HSBC Bank plc, Guernsey Branch, HSBC Bank plc in the Isle of Man, HSBC Continental Europe, Greece, The Hongkong and Shanghai Banking Corporation Limited, India (HSBC India), HSBC Bank (Vietnam) Limited, PT Bank HSBC Indonesia (HBID), HSBC Bank (Uruguay) S.A. (HSBC Uruguay is authorised and oversought by Banco Central del Uruguay), HBAP Sri Lanka Branch, The Hongkong and Shanghai Banking Corporation Limited – Philippine Branch, HSBC Investment and Insurance Brokerage, Philippines Inc, and HSBC FinTech Services (Shanghai) Company Limited and HSBC Mexico, S.A. Multiple Banking Institution HSBC Financial Group (collectively, the “Distributors”) to their respective clients. This document or video is for general circulation and information purposes only.
The contents of this document or video may not be reproduced or further distributed to any person or entity, whether in whole or in part, for any purpose. This document or video must not be distributed in any jurisdiction where its distribution is unlawful. All non-authorised reproduction or use of this document or video will be the responsibility of the user and may lead to legal proceedings. The material contained in this document or video is for general information purposes only and does not constitute investment research or advice or a recommendation to buy or sell investments. Some of the statements contained in this document or video may be considered forward looking statements which provide current expectations or forecasts of future events. Such forward looking statements are not guarantees of future performance or events and involve risks and uncertainties. Actual results may differ materially from those described in such forward-looking statements as a result of various factors. HBAP and the Distributors do not undertake any obligation to update the forward-looking statements contained herein, or to update the reasons why actual results could differ from those projected in the forward-looking statements. This document or video has no contractual value and is not by any means intended as a solicitation, nor a recommendation for the purchase or sale of any financial instrument in any jurisdiction in which such an offer is not lawful. The views and opinions expressed are based on the HSBC Global Investment Committee at the time of preparation and are subject to change at any time. These views may not necessarily indicate HSBC Asset Management‘s current portfolios’ composition. Individual portfolios managed by HSBC Asset Management primarily reflect individual clients’ objectives, risk preferences, time horizon, and market liquidity.
The value of investments and the income from them can go down as well as up and investors may not get back the amount originally invested. Past performance contained in this document or video is not a reliable indicator of future performance whilst any forecasts, projections and simulations contained herein should not be relied upon as an indication of future results. Where overseas investments are held the rate of currency exchange may cause the value of such investments to go down as well as up. Investments in emerging markets are by their nature higher risk and potentially more volatile than those inherent in some established markets. Economies in emerging markets generally are heavily dependent upon international trade and, accordingly, have been and may continue to be affected adversely by trade barriers, exchange controls, managed adjustments in relative currency values and other protectionist measures imposed or negotiated by the countries with which they trade. These economies also have been and may continue to be affected adversely by economic conditions in the countries in which they trade. Investments are subject to market risks, read all investment related documents carefully.
This document or video provides a high-level overview of the recent economic environment and has been prepared for information purposes only. The views presented are those of HBAP and are based on HBAP’s global views and may not necessarily align with the Distributors’ local views. It has not been prepared in accordance with legal requirements designed to promote the independence of investment research and is not subject to any prohibition on dealing ahead of its dissemination. It is not intended to provide and should not be relied on for accounting, legal or tax advice. Before you make any investment decision, you may wish to consult an independent financial adviser. In the event that you choose not to seek advice from a financial adviser, you should carefully consider whether the investment product is suitable for you. You are advised to obtain appropriate professional advice where necessary.
The accuracy and/or completeness of any third-party information obtained from sources which we believe to be reliable might have not been independently verified, hence Customer must seek from several sources prior to making investment decision.
The following statement is only applicable to HSBC Mexico, S.A. Multiple Banking Institution HSBC Financial Group with regard to how the publication is distributed to its customers: This publication is distributed by Wealth Insights of HSBC México, and its objective is for informational purposes only and should not be interpreted as an offer or invitation to buy or sell any security related to financial instruments, investments or other financial product. This communication is not intended to contain an exhaustive description of the considerations that may be important in making a decision to make any change and/or modification to any product, and what is contained or reflected in this report does not constitute, and is not intended to constitute, nor should it be construed as advice, investment advice or a recommendation, offer or solicitation to buy or sell any service, product, security, merchandise, currency or any other asset.
Receiving parties should not consider this document as a substitute for their own judgment. The past performance of the securities or financial instruments mentioned herein is not necessarily indicative of future results. All information, as well as prices indicated, are subject to change without prior notice; Wealth Insights of HSBC Mexico is not obliged to update or keep it current or to give any notification in the event that the information presented here undergoes any update or change. The securities and investment products described herein may not be suitable for sale in all jurisdictions or may not be suitable for some categories of investors.
The information contained in this communication is derived from a variety of sources deemed reliable; however, its accuracy or completeness cannot be guaranteed. HSBC México will not be responsible for any loss or damage of any kind that may arise from transmission errors, inaccuracies, omissions, changes in market factors or conditions, or any other circumstance beyond the control of HSBC. Different HSBC legal entities may carry out distribution of Wealth Insights internationally in accordance with local regulatory requirements.
Important Information about the Hongkong and Shanghai Banking Corporation Limited, India (“HSBC India”)
HSBC India is a branch of The Hongkong and Shanghai Banking Corporation Limited. HSBC India is a distributor of mutual funds and referrer of investment products from third party entities registered and regulated in India. HSBC India does not distribute investment products to those persons who are either the citizens or residents of United States of America (USA), Canada or New Zealand or any other jurisdiction where such distribution would be contrary to law or regulation.
The following statement is only applicable to HSBC Bank (Taiwan) Limited with regard to how the publication is distributed to its customers: HSBC Bank (Taiwan) Limited (“the Bank”) shall fulfill the fiduciary duty act as a reasonable person once in exercising offering/conducting ordinary care in offering trust services/ business. However, the Bank disclaims any guarantee on the management or operation performance of the trust business.
The following statement is only applicable to PT Bank HSBC Indonesia (“HBID”): PT Bank HSBC Indonesia (“HBID”) is licensed and supervised by Indonesia Financial Services Authority (“OJK”). Customer must understand that historical performance does not guarantee future performance. Investment product that are offered in HBID is third party products, HBID is a selling agent for third party product such as Mutual Fund and Bonds. HBID and HSBC Group (HSBC Holdings Plc and its subsidiaries and associates company or any of its branches) does not guarantee the underlying investment, principal or return on customer investment. Investment in Mutual Funds and Bonds is not covered by the deposit insurance program of the Indonesian Deposit Insurance Corporation (LPS).
Important information on ESG and sustainable investing
Today we finance a number of industries that significantly contribute to greenhouse gas emissions. We have a strategy to help our customers to reduce their emissions and to reduce our own. For more information visit www.hsbc.com/sustainability.
In broad terms “ESG and sustainable investing” products include investment approaches or instruments which consider environmental, social, governance and/or other sustainability factors to varying degrees. Certain instruments we classify as sustainable may be in the process of changing to deliver sustainability outcomes. There is no guarantee that ESG and Sustainable investing products will produce returns similar to those which don’t consider these factors. ESG and Sustainable investing products may diverge from traditional market benchmarks. In addition, there is no standard definition of, or measurement criteria for, ESG and Sustainable investing or the impact of ESG and Sustainable investing products. ESG and Sustainable investing and related impact measurement criteria are (a) highly subjective and (b) may vary significantly across and within sectors.
HSBC may rely on measurement criteria devised and reported by third party providers or issuers. HSBC does not always conduct its own specific due diligence in relation to measurement criteria. There is no guarantee: (a) that the nature of the ESG / sustainability impact or measurement criteria of an investment will be aligned with any particular investor’s sustainability goals; or (b) that the stated level or target level of ESG / sustainability impact will be achieved. ESG and Sustainable investing is an evolving area and new regulations are being developed which will affect how investments can be categorised or labelled. An investment which is considered to fulfil sustainable criteria today may not meet those criteria at some point in the future.
THE CONTENTS OF THIS DOCUMENT OR VIDEO HAVE NOT BEEN REVIEWED BY ANY REGULATORY AUTHORITY IN HONG KONG OR ANY OTHER JURISDICTION. YOU ARE ADVISED TO EXERCISE CAUTION IN RELATION TO THE INVESTMENT AND THIS DOCUMENT OR VIDEO. IF YOU ARE IN DOUBT ABOUT ANY OF THE CONTENTS OF THIS DOCUMENT OR VIDEO, YOU SHOULD OBTAIN INDEPENDENT PROFESSIONAL ADVICE.
© Copyright 2025. The Hongkong and Shanghai Banking Corporation Limited, ALL RIGHTS RESERVED.
No part of this document or video may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, on any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or otherwise, without the prior written permission of The Hongkong and Shanghai Banking Corporation Limited.